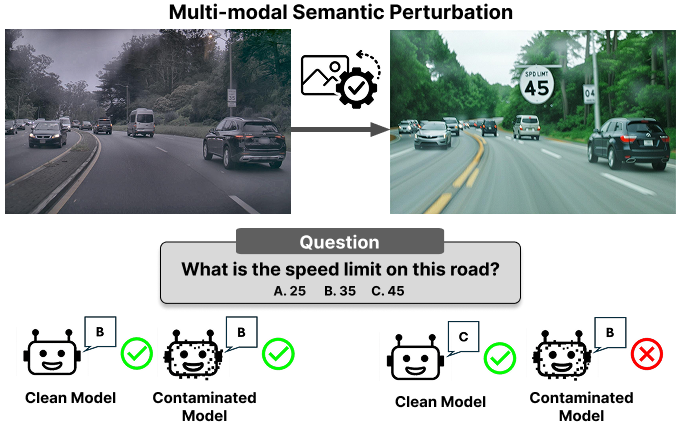
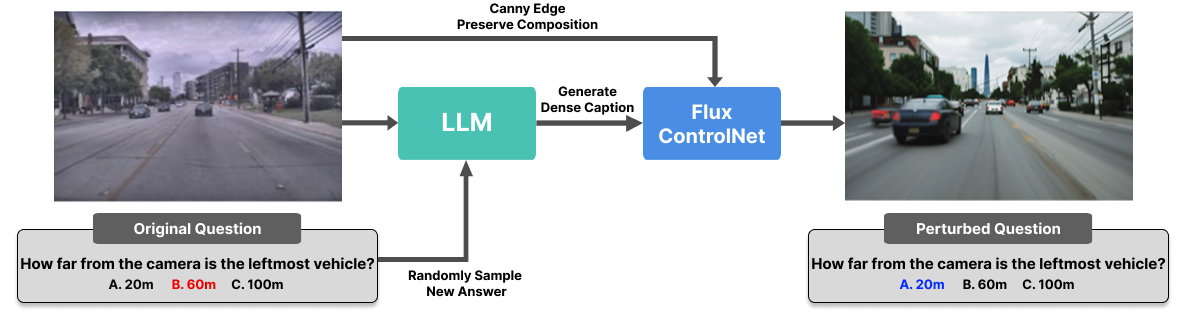
Real-world Counterfactuals.
We use
NaturalBench, a dataset consisting of natural adversarial counterfactual examples. We simulate our pipeline by training on one varaint of the counterfactuals and evaluating on the other variant.
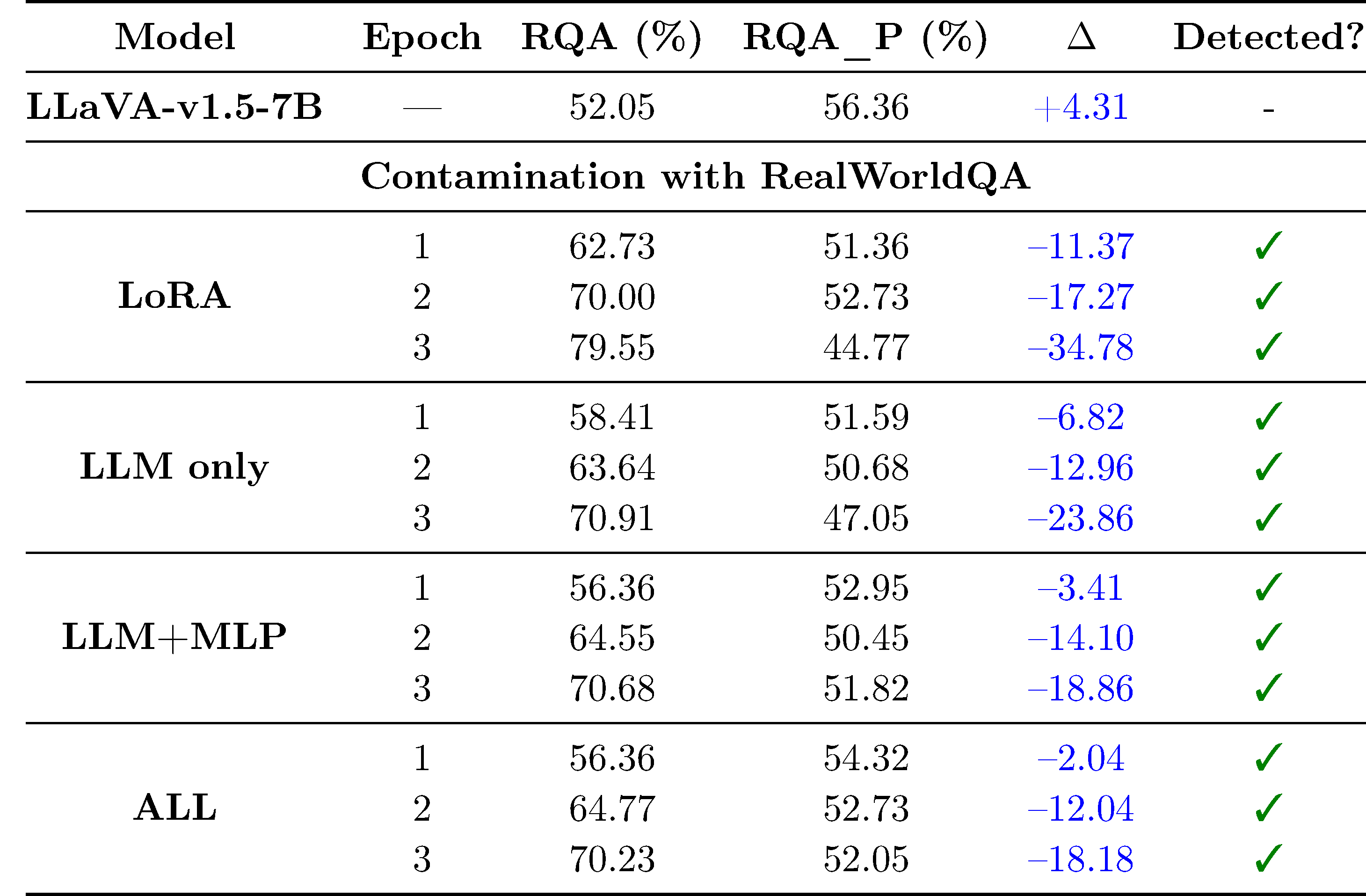
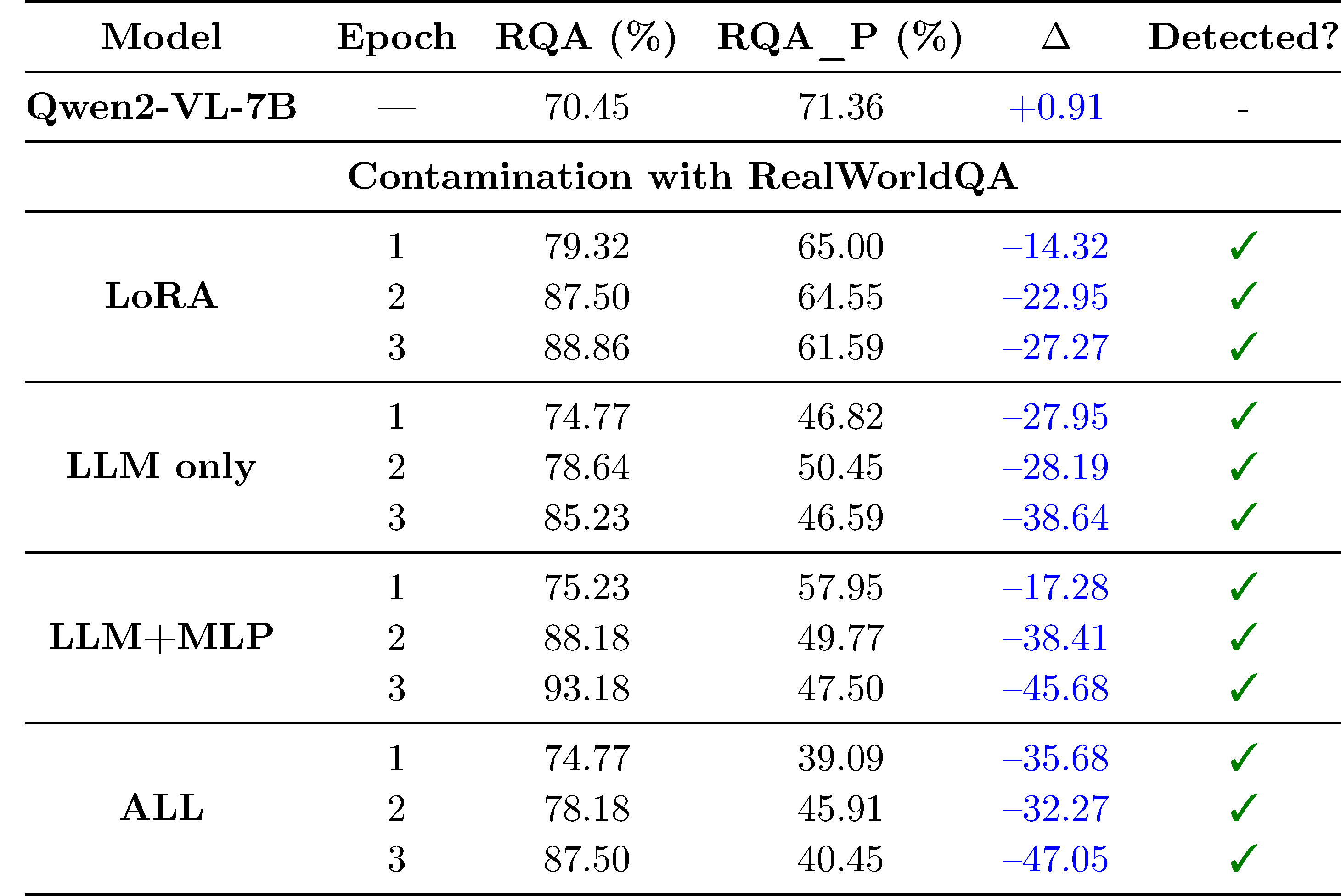
We observe that clean models show similar performance on both variants, while contaminated models show dramatic performance drops up to -45.58% (98.63% -> 53.05%). Note that this is a two-way multiple choice benchmark, meaning that a contaminated model with near perfect performance on the leaked data performs as bad as random guessing on the perturbed variant.
This result suggests that any reliable semantic variation - natural, procedural, or synthetic - fits our framework.
Our pipeline detects contamination with paraphrased data.
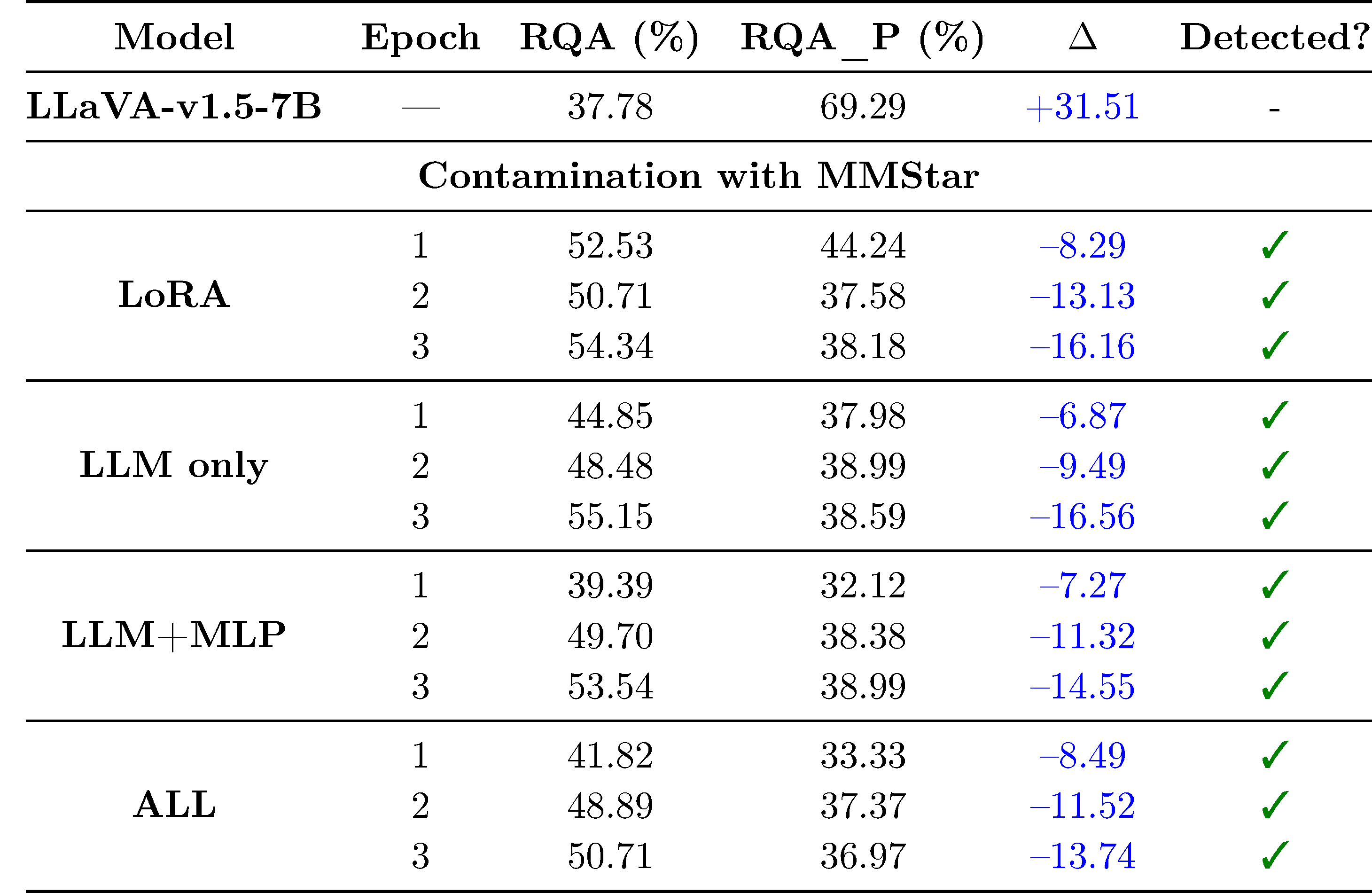
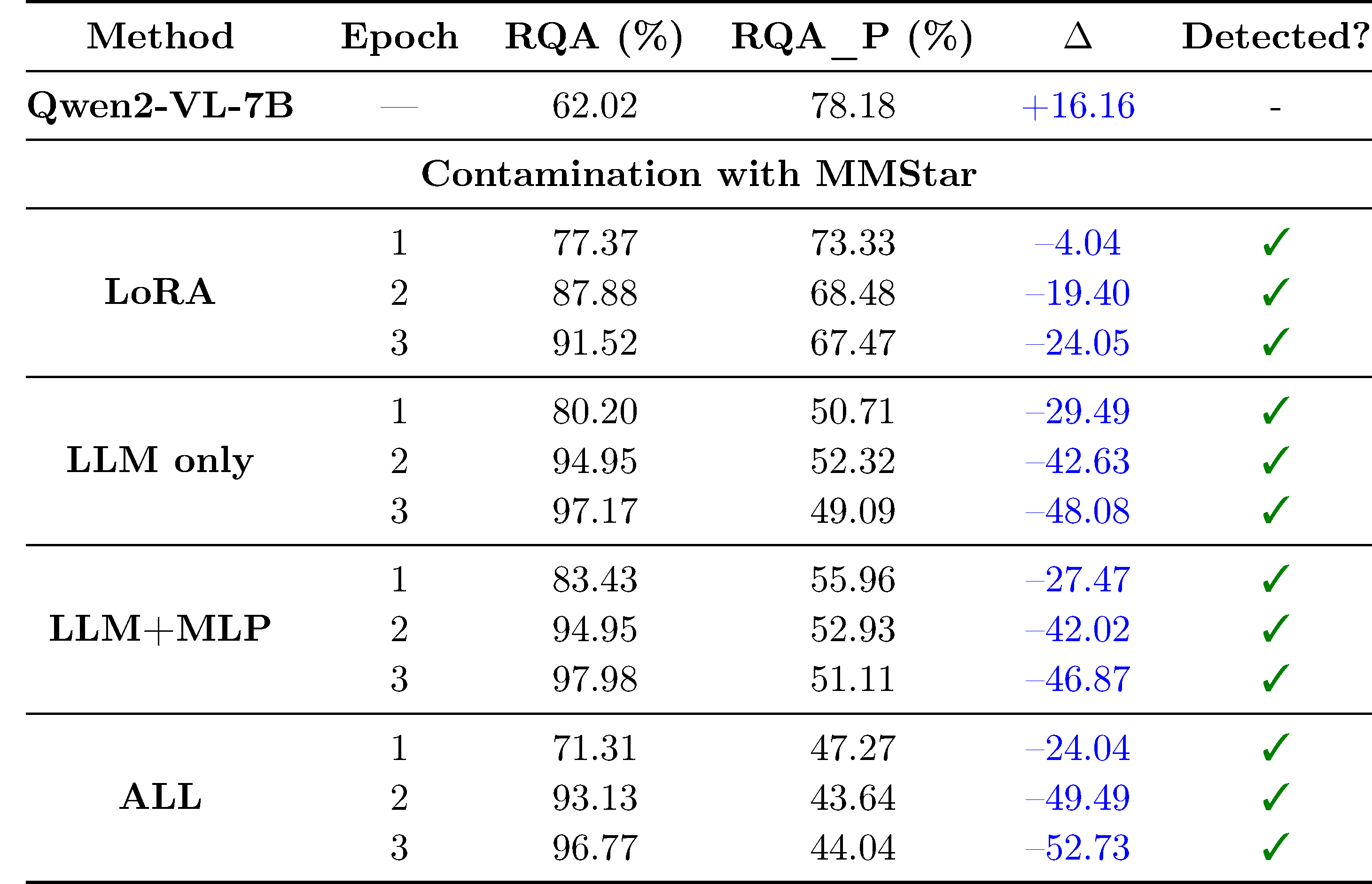
A simple but effective contamiation strategy is paraphrasing the training data. We verify that our approach can detect models that have been contaminated with paraphrased data.
Our pipeline is modular.
For our main experiments, we use GPT-4o as the LLM and Flux ControlNet as the text-to-image model. However, we verify that our approach works even after replacing GPT-4o with Molmo-7B-D, and after replacing manual filtering with verification by a strong reasoning model like
o3.
Our pipeline generalizes to pretraining and larger models.
We verify that our approach can detect contamination that occurs during the pretraining stage, when LLaVA-v1.5-7B is trained from scratch. We also verify that our approach extends to larger models like LLaVA-v1.5-13B.
Our pipeline generalizes beyond multi-choice VQA settings.
Our framework is not inherently tied to the multiple-choice VQA setting. Once visual evidence is perturbed, the evaluation can be adapted to other tasks using string matching, likelihood-based scoring, or LLM-as-a-judge approaches. We show that our approach can be extended to free-form QA in the appendix.